Hirotaka Takahashi
Development of small chemical compounds that specifically inhibited USP-family deubiquitinating enzymes.
 |
Hirotaka Takahashi, PhD.Division of Cell-free Sciences, Proteo-Science Center, Ehime University. |
|---|
Research summary
Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) are proteases that remove ubiquitin from ubiquitinated proteins, and cleave polyubiquitin chains. DUBs regulated various kinds of cellular events by protection of proteins from proteolysis by 26S proteasome and regulation of ubiquitin-dependent signal transductions. Recently it has been reported that overexpression of DUBs leads to the abnormal accumulation of proteins to be degraded, resulting in cause of many diseases such as cancers and neurological diseases. Therefore, DUB is thought to be as attractive targets for drug discovery.
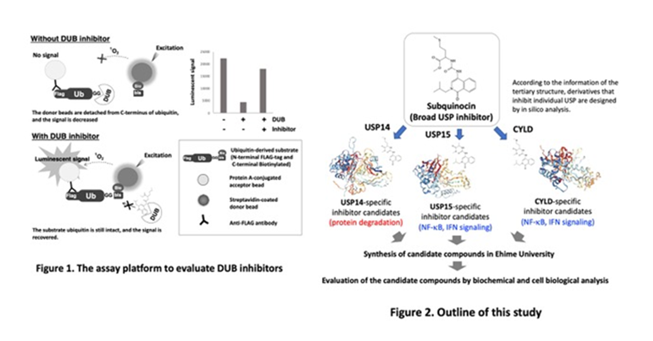
In this study, based on a wheat cell-free protein synthesis system (wheat cell-free system) that has been developed in Proteo-Science Center in Ehime University, we established a biochemical platform to screen the DUB inhibitors in a high-throughput manner and to evaluate the selectivity of the DUB inhibitor using more than 40 human recombinant DUB proteins. In our preceding studies, we found a unique chemical compound named Subquinocin, which bound to a region conserved in catalytic domain of USP, and inhibited only USP family DUBs. About 100 DUBs are encoded in human genome, and more than half of these DUBs belong to the USP family including many physiologically important DUBs.
In this project, we aim to develop the derivative compounds of Subquinocin that specifically inhibited target USP, based on the in silico analysis. We selected three USPs, USP14 that is involved in the protein degradation, and USP15 and CYLD that are involved in various kinds of inflammation and immune responses, as first target USPs. The derivative compounds of Subquinocin are selected by the in silico analysis, and inhibitory effects of these compounds on these three USPs are evaluated by the biochemical evaluation described above. The structures of the hit compounds are further improved according to the result of in silico analysis and the biochemical evaluations. The obtained derivative compounds that specifically inhibited individual USPs are expected to become useful chemical probe to know the distinct cellular functions of these USPs, as well as to provide important information for drug discovery. Through this research project, we aim to contribute to many research activities to develop the specific DUB inhibitors in academic field or drug industries.
Publications
- Uematsu A, Kido K, Takahashi H, Takahashi C, Yanagihara Y, Saeki N, Yoshida S, Maekawa M, Honda M, Kai T, Shimizu K, Higashiyama S, Imai Y, Tokunaga F, *Sawasaki T.
The E3 ubiquitin ligase MIB2 enhances inflammation by degrading the deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD.
J. Biol. Chem. 294, 14135–14148 (2019)
PMID: 31366726 - Nomura S, Takahashi H, Suzuki J, Kuwahara M, Yamashita M, *Sawasaki T.
Pyrrothiogatain acts as an inhibitor of GATA family proteins and inhibits Th2 cell differentiation in vitro.
Sci. Rep. 9,17335 (2019)
PMID: 31758034 - Yamanaka S, Sato Y, Oikawa D, Goto E, Fukai S, Tokunaga F, *Takahashi H, *Sawasaki T.
Subquinocin, a small molecule inhibitor of CYLD and USP-family deubiquitinating enzymes, promotes NF-κB signaling.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 524, 1-7 (2020)
PMID: 31898971 -
*Takahashi H, Yamanaka S, Kuwada S, Higaki K, Kido K, Sato Y, Fukai S, Tokunaga F, *Sawasaki T.
A Human DUB Protein Array for Clarification of Linkage Specificity of Polyubiquitin Chain and Application to Evaluation of Its Inhibitors.
Biomedicines 8, 152 (2020)
PMID: 32512835 - Inoue S, Kaiserli E, Zhao X, Waksman T, Takemiya A, Okumura M, Takahashi H, Seki S, Shinozaki K, Endo Y, Sawasaki T, Kinoshita T, Zhang X, Christie J, Shimazaki K.
CIPK23 regulates blue light-dependent stomatal opening in Arabidopsis thaliana.
Plant J. 104, 679-692 (2020)
PMID: 32780529 - Nakabayashi O, Takahashi H, Moriwaki K, Komazawa-Sakon S, Ohtake F, Murai S, Tsuchiya Y, Koyahara Y, Saeki Y, Yoshida Y, Yamazaki S, Tokunaga F, Sawasaki T, Nakano H.
MIND Bomb 2 prevents TNF-induced apoptosis via two distinct mechanisms.
Commun. Biol. 4, 80 (2021)
PMID: 33469115 - Yamanaka S, Murai H, Saito D, Abe G, Tokunaga E, Iwasaki T, Takahashi H, Takeda H, Suzuki T, Shibata N, Tamura K, Sawasaki T.
Thalidomide and its metabolite 5-hydroxythalidomide induce teratogenicity via the cereblon neo-substrate PLZF.
EMBO journal. 40, e105375 (2021)
PMID: 33470442
Former Publications
- Takahashi H, Nozawa A, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Endo Y, *Sawasaki T.
A simple and high-sensitivity method for analysis of ubiquitination and polyubiquitination based on wheat cell-free protein synthesis.
BMC Plant Biol. 9, 39 (2009)
PMID: 19348673 - Takahashi H, Ozawa A, Nemoto K, Nozawa A, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Takeda H, Endo Y, *Sawasaki T.
Genome-wide biochemical analysis of Arabidopsis protein phosphatase using a wheat cell-free system.
FEBS Lett. 586, 3134-3141 (2012)
PMID: 22968126 - Takahashi H, Takahashi C, Moreland NJ, Chang Y-T, Sawasaki T, Ryo A, Vasudevan SG, *Suzuki Y, *Yamamoto N.
Establishment of a robust dengue virus NS3-NS5 binding assay for identification of protein-protein interaction inhibitors.
Antiviral Res. 96, 305-314 (2012)
PMID: 23072882 - Takahashi H, Nemoto K, Ramadan A, *Sawasaki T.
Technology of wheat cell-free based protein array for biochemical analyses of protein kinases and ubiquitin E3 ligases. In: Inoue J, Takekawa M (eds)
Protein Modifications in Pathogenic Dysregulation of Signaling.Springer Japan, 43-60 (2015) - Takahashi H, Uematsu A, Yamanaka S, Imamura M, Nakajima T, Doi K, Yasuoka S, Takahashi C, Takeda H, *Sawasaki T.
Establishment of a Wheat Cell-Free Synthesized Protein Array Containing 250 Human and Mouse E3 Ubiquitin Ligases to Identify Novel Interaction between E3 Ligases and Substrate Proteins.
PLoS ONE 11, e0156718 (2016)
PMID: 27249653 - Yonezawa T, Takahashi H, Shikata S, Sawasaki T, Kitamura T, Goyama S.
The ubiquitin ligase RNF38 promotes RUNX1 ubiquitination and enhances RUNX1-mediated suppression of erythroid transcription program.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.505, 905-909 (2018)
PMID: 30309654