Maiko Okada
Development of high sensitive array of the linkage-specific ubiquitin aptamers
 |
Maiko Okada, PhDTokyo University of Technology, School of Bioscience and Biotechnology |
|---|
Research summary
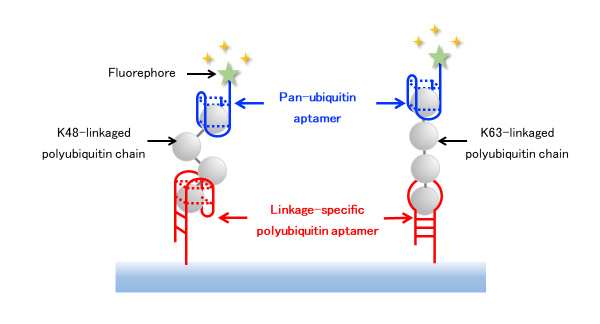
The diversity of poly-ubiquitination encodes various cellular process lead to physiological function. Therefore, to elucidate the detailed molecular mechanisms, it is necessary to develop a molecular recognition element available for the identification of ubiquitin-linkage specificity.
In this study, we aim to obtain the aptamers linkage-specific to ubiquitin chain alternatives to antibodies and apply them to highly sensitive aptamer arrays.
Former Publications
- Chen ST, Okada M, Nakato R, Izumi K, Bando M, *Shirahige K.
The Deubiquitinating Enzyme USP7 regulates Androgen Receptor Activity by Modulating Its Binding to Chromatin.
J. Biol. Chem. 290, 21713-21723 (2015)
PMID: 26175158 - Okada M, Ohtake F, Nishikawa H, Wu W, Saeki Y, Tanaka K, *Ohta T.
Liganded ERα stimulates the E3 ubiquitin ligase activity of UBE3C to facilitate cell proliferation.
Mol. Endocrinol. 29, 1646-1657 (2015)
PMID: 26389696 - Nakajima S, *Watashi K, Ohashi H, Kamisuki S, Izaguirre-Carbonell J, Kwon AT, Suzuki H, Kataoka M, Tsukuda S, Okada M, Moi ML, Takeuchi T, Arita M, Suzuki R, Aizaki H, Kato T, Suzuki T, Hasegawa H, Takasaki T, Sugawara F, Wakita T.
Fungus-derived neoechinulin B as a novel antagonist of liver X receptor, identified by chemical genetics using hepatitis C virus cell culture system.
J. Virol. 90, 9058-9074 (2016)
PMID: 27489280 - Tsuruga T, Kumai T, *Okada M.
UBE3B and UBE3C functionally regulate cell proliferation through the ubiquitin-proteasome system.
J. St. Marianna Univ. 45, 149-159 (2017) - Tamura S, Okada M, Kato S, Shinoda N, Fukunaga K, Ui-Tei K, *Ueda M.
Ouabagenin is a naturally occurring LXR ligand without causing hepatic steatosis as a side effect.
Sci. Rep. 8, 2305 (2018)
PMID: 29396543