Daisuke Oikawa
Pathobiochemical analysis using chemo-technologies targeting linear ubiquitin chain
 |
Daisuke Oikawa, PhDDepartment of Pathobiochemistry, Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka City University. |
|---|
Research summary
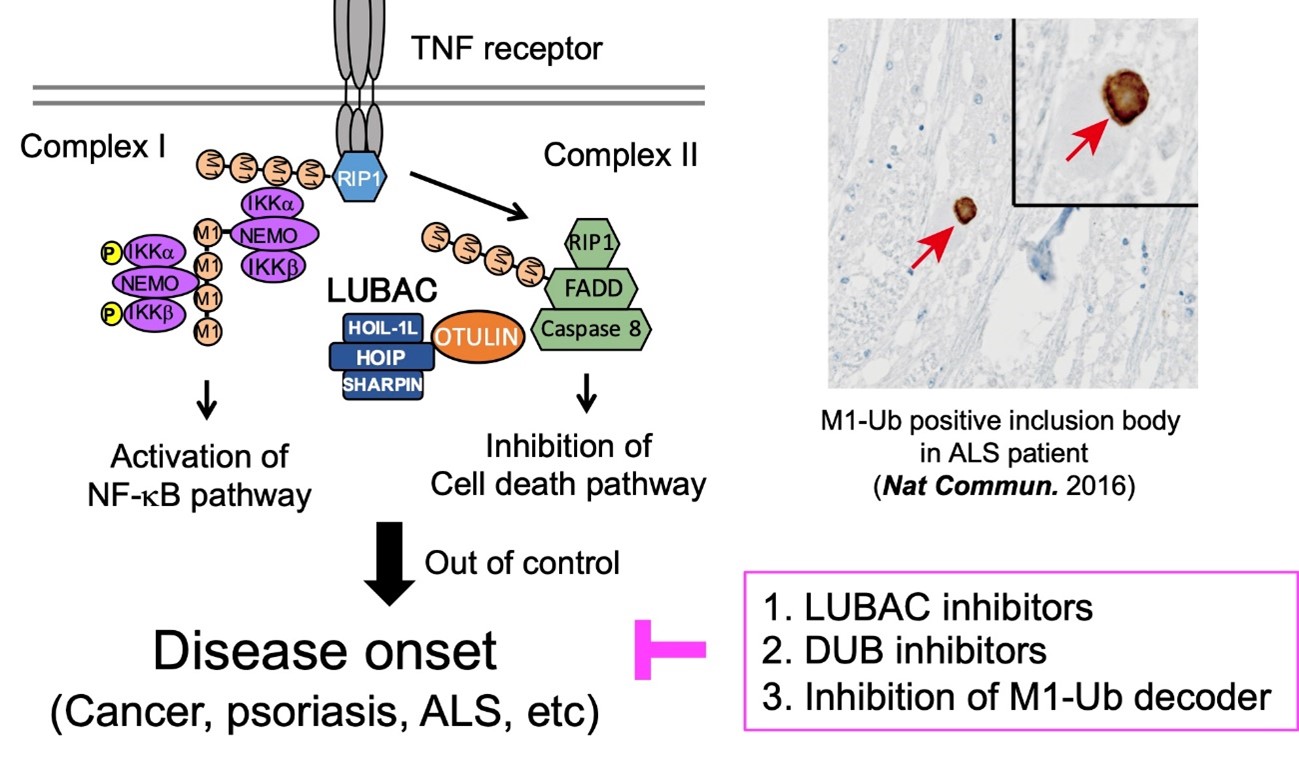
A distinct type of ubiquitination characterized by an inter-ubiquitin linkage through the N-terminal methionine is called M1-linked or linear ubiquitination. Linear ubiquitin chains are assembled by LUBAC ubiquitin ligase complex, composed of the HOIP, HOIL-1L, and SHARPIN. Furthermore, LUBAC has been found to be associated with OTULIN and CYLD, deubiquitinases that disassemble linear chains and counterbalance the E3 ligase activity of LUBAC. Formation, recognition, and disassembly of linear ubiquitin chains are highly specific processes that are implicated in immune signaling, cell death regulation and protein quality control. We previously identified that OPTN (optineurin) regulates both NF-κB activation and apoptosis via linear ubiquitin binding, and the disruption of these cellular functions is involved in ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis) pathogenesis. Also, many recent reports indicate that autosomal defects in LUBAC are associated with both autoinflammation and immunodeficiency in humans, with additional disorders described in mice. Thus, linear ubiquitin chains would contribute to the pathogenesis of various human diseases.
Here, we will construct chemo-technology tools targeting the linear ubiquitin chain, including a development of specific inhibitors for LUBAC, or deubiquitinases that disassemble the linear chains. With the novel chemo-tools, we will perform pathobiochemical analysis in vitro, in cells, and in animal model, to reveal the molecular mechanism and physiological function of linear ubiquitin chains.
Publications
- Yamanaka S, Sato Y, Oikawa D, Goto E, Fukai S, Tokunaga F, *Takahashi H, *Sawasaki T.
Subquinocin, a small molecule inhibitor of CYLD and USP-family deubiquitinating enzymes, promotes NF-κB signaling.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 524, 1-7 (2020)
PMID: 31898971 - Oikawa D, Sato Y, Ohtake F, Komakura K, Hanada K, Sugawara K, Terawaki S, Mizukami Y, Phuong HT, Iio K, Obika S, Fukushi M, Irie T, Tsuruta D, Sakamoto S, Tanaka K, Saeki Y, Fukai S, *Tokunaga F.
Molecular bases for HOIPINs-mediated inhibition of LUBAC and innate immune responses.
Commun. Biol. 3, 163 (2020)
PMID: 32246052 - Kuriyama Y, *Shimizu A, Kanai S, Oikawa D, Tokunaga F, Tsukagoshi H, Ishikawa O.
The synchronized gene expression of retrotransposons and type I interferon in dermatomyositis.
J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 84, 1103-1105 (2020)
PMID: 32439465 - Oikawa D, Hatanaka N, Suzuki T, *Tokunaga F.
Cellular and Mathematical Analyses of LUBAC Involvement in T Cell Receptor-mediated NF-kB Activation Pathway.
Front Immunol. 11, 601926 (2020)
PMID: 33329596 - Dat NQ, Thuy LTT, Hieu VN, Hai H, Hoang DV, Hai NTT, Thuy TTV, Komiya T, Rombouts K, Phuong DM, Hanh NV, Hoang TH, Sato-Matsubara M, Oikawa D, Yoishizato K, Tokunaga F, Pinzani M, *Kawada M.
His-Cytoglobin Deactivates Hepatic Stellate Cells and Inhibits Liver Fibrosis by Scavenging Reactive Oxygen Species.
Hepatology. AOP (2021) - *Iwasaki N, Terawaki S, Shimizu K, Oikawa D, Sakamoto H, Sunami K, Tokunaga F.
Th2 cells and macrophages cooperatively induce allergic inflammation through histamine signaling.
PLoS One. 16, e0248158 (2021)
PMID: 33662037 - Miyashita H, Oikawa D, Terawaki S, Kabata D, Shintani A, *Tokunaga F.
Crosstalk between NDP52 and LUBAC in innate immune responses, cell death, and xenophagy.
Front Immunol. AOP (2021)
Former Publications
- *Iwawaki T, Akai R, Oikawa D, Toyoshima T, Yoshino M, Suzuki M, Takeda N, Ishikawa T, Kataoka Y, Yamamura K.
Transgenic mouse model for imaging of interleukin-1β-related inflammation in vivo.
Sci. Rep. 5, 17205 (2015)
PMID: 26598133 - Nakazawa S+, Oikawa D+, Ishii R+, Ayaki T, Takahashi H, Takeda H, Ishitani R, Kamei K, Izumi T, Kawakami H, Iwai K, Hatada I, Sawasaki T, *Ito H, *Nureki O, *Tokunaga F.
Linear ubiquitination is involved in the pathogenesis of optineurin-associated amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Nat. Commun. 7, 12547 (2016)
PMID: 27552911 - Hattori M, Ishikawa O, Oikawa D, Amano H, Yasuda M, Kaira K, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Nakano H, Sawamura D, Terawaki S, Wakamatsu K, Tokunaga F, *Shimizu A.
In-frame Val 216-Ser 217 deletion of KIT in mild piebaldism causes aberrant secretion and SCF response.
J. Dermatol. Sci. 91, 35-42 (2018)
PMID: 29631773 - Oikawa D, *Shiota M, Goto E, Komakura K, Wanibuchi H, *Tokunaga F.
Generation of Rat Monoclonal Antibodies Against a Deubiquitinase, Ovarian Tumor Domain-Containing Protein 1.
Monoclon. Antib. Immunodiagn. Immunother. 37, 180-184 (2018)
PMID: 30130141 - *Katsuya K, Hori Y, Oikawa D, Yamamoto T, Umetani K, Urashima T, Kinoshita T, Ayukawa K, Tokunaga F, Tamaru M.
High-Throughput Screening for Linear Ubiquitin Chain Assembly Complex (LUBAC) Selective Inhibitors using Homogenous Time- Resolved Fluorescence (HTRF)-Based Assay System.
SLAS Discov. 23, 1018-1029 (2018)
PMID: 30071751 - Kato K, *Nishimasu H, Oikawa D, Hirano S, Hirano H, Ishitani R, Tokunaga F, Kasuya G, *Nureki O.
Structural insights into cGAMP degradation by Ecto-nucleotide pyrophosphatase phosphodiesterase 1.
Nat. Commun. 9, 4424 (2018)
PMID: 30356045 - Katsuya K+, Oikawa D+, Iio, K, Obika S, Hori Y, Urashima T, Ayukawa K, *Tokunaga F.
Small-molecule inhibitors of linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex (LUBAC), HOIPINs, suppress NF-κB signaling.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 509, 700-706 (2019)
PMID: 30611571