Shin Mizukami
Spatiotemporal regulation of proteolysis based on photoreversible protein labeling technology
 |
Shin Mizukami, PhDTohoku University, Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials |
|---|
Research summary
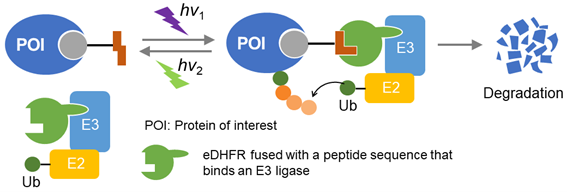
Selective degradation technologies for intracellular proteins using the ubiquitin-proteasome system (PROTACs/SNIPERs) have attracted increasing attentions. If these methods are further developed and the reversible light control of protein knockdown is achieved, the quantity of the target protein can be spatiotemporally regulated. This innovative technology will be applied to the various cell biological fields. As a clue to achieve that, we recently reported a photoswitchable ligand azoMTX, which reversibly binds to E. coli dihydrofolate reductase (eDHFR). AzoMTX exhibits two photoisomerization states with different binding constants to eDHFR, and the isomers are reversibly converted to each other by irradiation at different wavelengths. In addition, the composition of the two states can be modulated by changing the wavelength of the illumination. Therefore, in this study, we aim to develop photoresponsive selective protein degradation based on the photoswitchable protein labeling system. As a photoswitchable analog of PROTACs, we will develop bifunctional photodegradation inducers with an azoMTX analog and a ligand for one of E3-ligases such as CRBN, VHL, and cIAP. As the proof of concept, a fluorescent protein is chosen as the target protein, and the degradation will be evaluated under a fluorescence microscope, as this optical system allows for illumination at specific wavelengths with high spatial and temporal resolution. In addition, quantitative regulation of intracellular target proteins will be challenged.
Publications
- Mashita T, Kowada T, Takahashi H, Matsui T, *Mizukami S.
Light-wavelength-based Quantitative Control of Dihydrofolate Reductase Activity Using Photochromic Isostere of Inhibitor.
ChemBioChem 20, 1382–1386 (2019)
PMID: 30656808 - Imoto T, Muramatsu M, Miyasaka H, Mizukami S, *Kikuchi K.
Improvement in Photostability of Fluorescein by Lanthanide Ions based on Energy Transfer-Based Triplet State Quenching.
Chem. Lett. 48, 1181–1184 (2019) - Kowada T, Watanabe T, Amagai Y, Liu R, Yamada M,Takahashi H, Matsui T, Inaba K, *Mizukami S.
Quantitative imaging of labile Zn2+ in the Golgi apparatus using a localizable small-molecule fluorescent probe.
Cell Chem. Biol. 27, 1521–1531 (2020)
PMID: 32997976 - Kowada T, Arai K, Yoshimura A, Matsui T, Kikuchi K, *Mizukami S.
Optical manipulation of subcellular protein translocation using a photoactivatable covalent labeling system.
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. AOP (2021)
PMID: 33644979 - Kowada T, Watanabe T, Liu R, *Mizukami S.
Protocol for synthesis and use of a turn-on fluorescent probe for quantifying labile Zn2+ in the Golgi Apparatus in live cells.
STAR Protoc. 2, 100395 (2021)
Former Publications
- Mizukami S, Hosoda M, Satake T, Okada S, Hori Y, Furuta T, *Kikuchi K.
Photocontrolled Compound Release System Using Caged Antimicrobial Peptide.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 9524–9525 (2010)
PMID: 20583831 - Mizukami S, Watanabe S, Akimoto Y, *Kikuchi K.
No-Wash Protein Labeling with Designed Fluorogenic Probes and Application to Real-Time Pulse-Chase Analysis.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 1623–1629 (2012)
PMID: 22224915 - Mizukami S, Hori Y, *Kikuchi K.
Small-Molecule Based Protein-Labeling Technology in Live Cell Studies: Probe-Design Concepts and Applications.
Acc. Chem. Res. 47, 247–256 (2014)
PMID: 23927788 - Matsui Y, Funato Y, Imamura H, Miki H, *Mizukami S, *Kikuchi K.
Visualization of Long-term Mg2+ Dynamics in Apoptotic Cells with a Novel Targetable Fluorescent Probe.
Chem. Sci. 8, 8255–8264 (2017)
PMID: 29619172