Masayuki Tera
Development of ubiquitin-proteasome inducer on the G-quadruplex
 |
Masayuki Tera, PhDInstitute of Engineering, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology |
|---|
Research summary
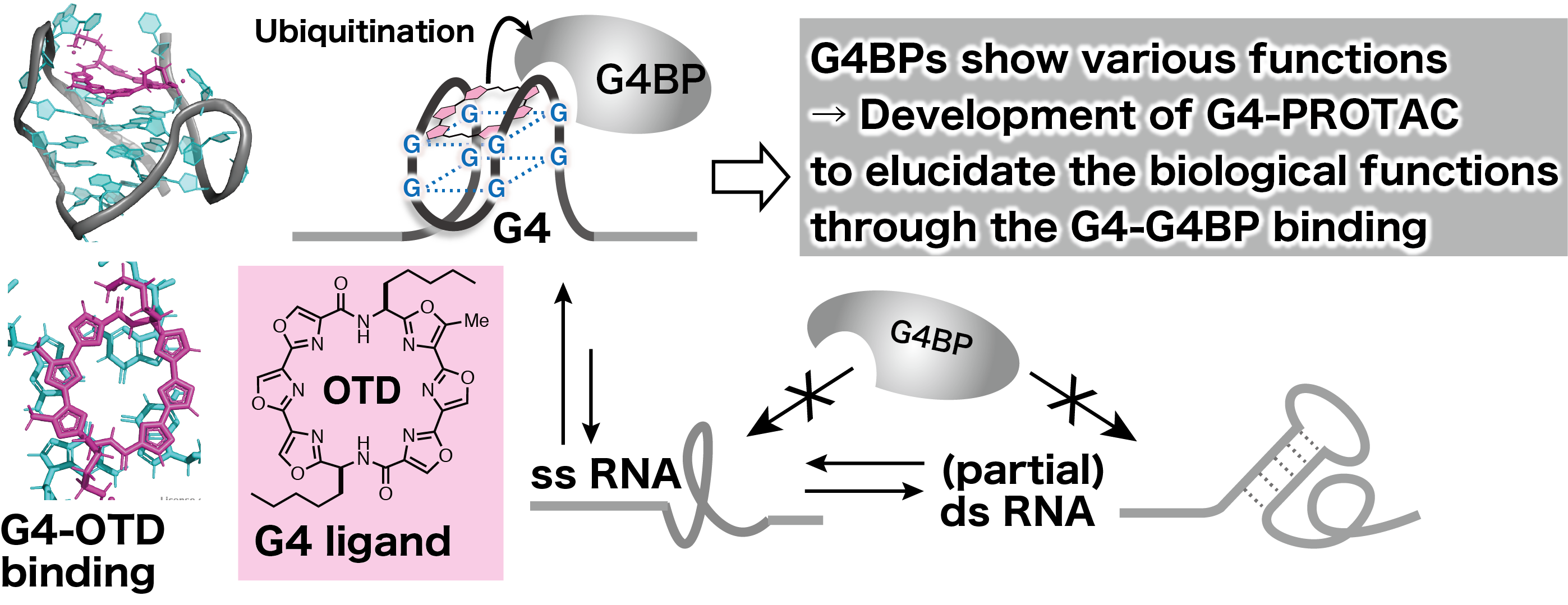
Guanine quadruplexes (G4) are higher-order nucleic acid structures formed by guanine-rich sequence, and G4-forming sequences are found at telomeres at the ends of chromosomes, gene promoters, and untranslated regions of RNA. In the cellular environment, G4s are thought to be dynamic conformation that are in equilibrium with single-stranded and partially double-stranded, and its equilibrium shifts to formation upon binding to G4 Binding Protein (G4BP) and small molecules (G4 ligands). G4 is attracting attention as a next-generation drug target and a new regulator of biological activities because it expresses biological functions based on its "three-dimensional structure" rather than on the sequence.
G4s are thought to be frequently formed in RNA due to the lack of complementary strands, and about 20 types of G4BPs have been identified so far, such as G4 helicase DHX 9, hnRNPs involved in splicing, and nucleolin involved in RNA stability and localization. Although G4BPs are thought to transiently regulate cellular functions in cooperation with dynamic G4, most of the reports are limited to binding studies with G4 oligoRNAs in cell-free systems, and the functions expressed by binding to G4 in living cells are still largely unknown. Although RNA-protein interactions have a significant impact on cellular functions, the methods for studying them are not as well established as those for protein-protein interactions. The G4 ligand we have developed will provide a new research tool for the analysis of RNA-protein interactions based on the ubiquitination of G4BP by G4-PROTAC and its associated proteasomal degradation.
In this study, we will first synthesize G4-PROTACs by synthetically linking azide G4 ligands (OTD, LCO, and BBRs) and E3 ligands via various linkers. Next, we will validate the ubiquitination reaction using G4 as a reaction field by combining readily available G4BP with RNA G4. Finally, G4-PROTACs will be applied to cultured cells to evaluate whether G4BPs are actually ubiquitinated on G4 and undergo chemical knockout. This will lead to the development of G4-PROTACs, a tool to elucidate the function of G4BP.
Publications
- Ishikawa R, Yasuda M, Sasaki S, Ma Y, Nagasawa K, *Tera M.
Stabilization of telomeric G-quadruplex by ligand binding increases susceptibility to S1 nuclease.
Chem. Commun. 57, 7236-7239 (2021)
PMID: 34263271 - Sasaki S, Kitamura J, Endo H, Shiraishi A, Ikebukuro K, Mizutani T, *Tera M.
Identification of G-quadruplex sequences in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Translat Regulat Sci.3,89-92 (2021) - Mizumoto Y, Sakamoto R, Nagata A, Sakane S, Kittaka A, Odagi M, Tera M, Nagasawa K.
Synthesis of C2-Alkoxy-Substituted 19-Nor Vitamin D 3 Derivatives: Stereoselectivity and Biological Activity
Biomolecules. 12, 69 (2022)
PMID: 35053217 - Kitagawa K, Okuma N, Yoshinaga M, Takemae H, Sato F, Sato S, Nakabayashi S, Yoshikawa H Y, Suganuma M, Luedtke N W, Matsuzaki T, *Tera M.
Ion-pair-enhanced double-click driven cell adhesion and altered expression of related genes.
Bioconjug. Chem. AOP (2023)
PMID: 36763006
Former Publications
- Tera M, Harati-Taji Z, *Luedtke N W.
Intercalation-Enhanced “Click” Crosslinking of DNA.
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 15405-15409 (2018)
PMID: 30240107 - Tera M, *Luedtke N W.
Three-Component Bioorthogonal Reactions on Cellular DNA and RNA.
Bioconjug. Chem. 30, 2991-2997 (2019)
PMID: 31697067 - *Tera M, Luedtke N W.
Cross-Linking Cellular Nucleic Acids via a Target-Directing Double Click Reagent.
Meth. Enzymol. 641, 433–457 (2020)
PMID: 32713534 - Yasuda M, Ma Y, Okabe S, Wakabayashi Y, Dongdong S, Young-Tae C, Seimiya H, *Tera M,*Nagasawa K.
Target identification of a macrocyclic hexaoxazole G-quadruplex ligand using a post-target-binding visualization.
Chem. Commun. 56, 12905-12908 (2020)
PMID: 33030187 - Sasaki S, Ma Y, Ishizuka T, Bao HL, Hirokawa T, Xu Y, Tera M,*Nagasawa K.
Linear consecutive hexaoxazoles as G4 ligands inducing chair-type anti-parallel topology of a telomeric G-quadruplex.
RSC Adv. 10, 43319–43323 (2020)