Daisuke Oikawa
Inhibition of disease pathogenesis using chemo-technologies targeting the linear ubiquitin chain-dynamics
 |
Daisuke Oikawa, PhDDepartment of Medical Biochemistry, Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka Metropolitan University |
|---|
Research summary
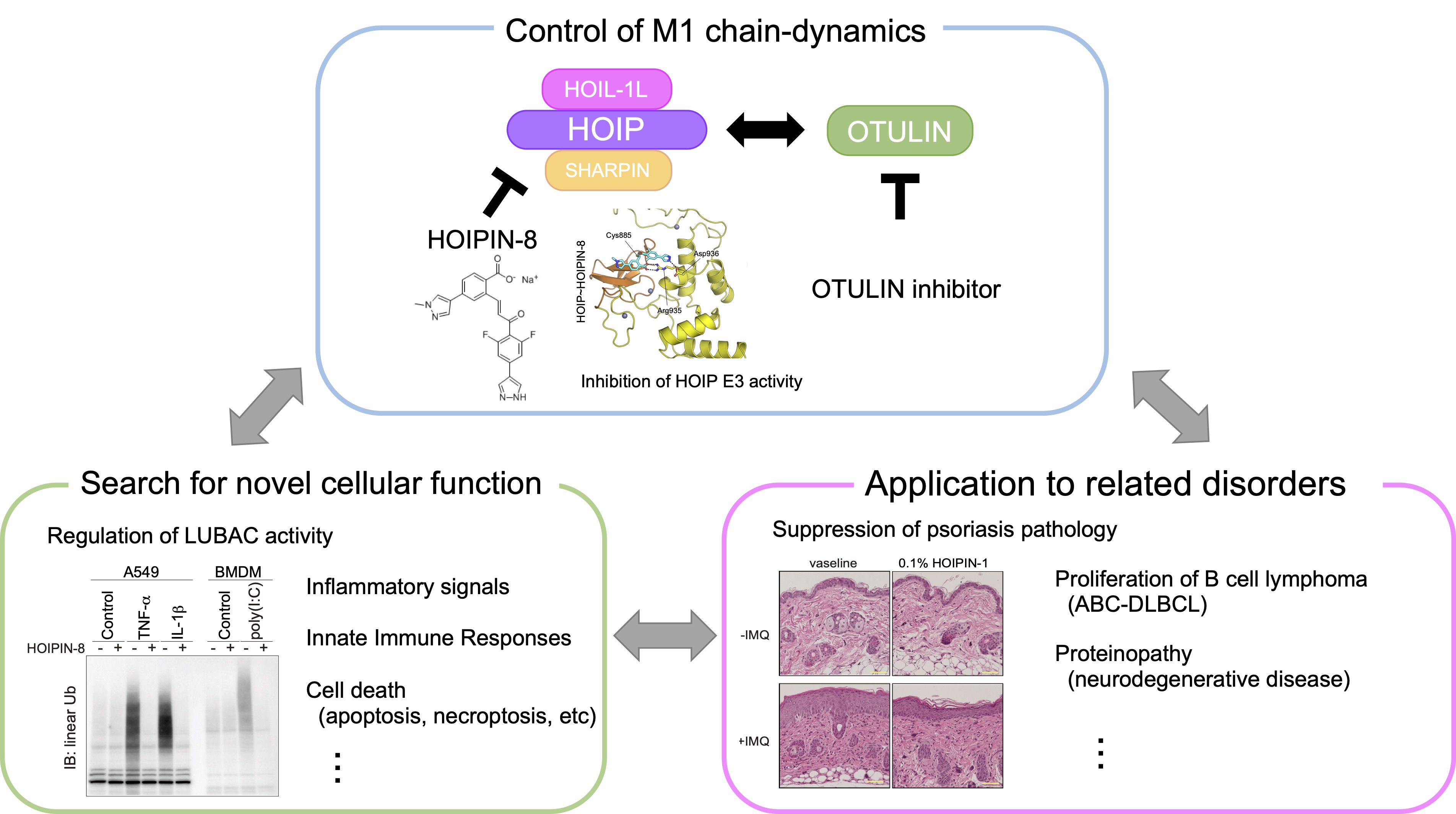
Linear ubiquitin chain (M1 chain), which is formed by a distinct linkage through the N-terminal methionine of ubiquitin molecule, regulates innate immune response and cell death. Also, recent reports indicate that the M1 chain is involved in the formation of protein aggregates. While the M1 chain is synthesized by LUBAC (linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex), which is composed of HOIL-1L, HOIP, and SHARPIN, it is degraded by deubiquitinating enzymes such as OTULIN. Thus, dynamics of the M1 chain is dually regulated by both the LUBAC and OTULIN.
Recently, we have developed HOIPIN-8, an inhibitor for LUBAC, and reported that HOIPIN-8 specifically inhibits LUBAC activity in vitro, and regulates innate immune responses and cell death at the cellular level in a LUBAC-dependent manner. Moreover, HOIPINs effectively suppressed the pathogenesis of B-cell lymphoma and mouse psoriasis models. In this study, we will control the dynamics of M1 chain through the development of OTULIN inhibitors in addition to HOIPIN-8, explore the novel physiological function of the M1 chain, and elucidate the inhibitory effect and molecular mechanism for the pathogenesis of various related disorders.
1) Development of OTULIN inhibitors and cellular analysis
We will accelerate the development of OTULIN inhibitors, which we are currently working on, by elucidating their specificity and structural basis through joint research. Also, we will evaluate their functionality by comparing their effects on various signaling pathways with those of OTULIN-KO cells. Furthermore, we will explore the novel physiological function of the M1 chain by using both HOIPIN-8 and OTULIN inhibitors.
2) Evaluation of the inhibitory effect of HOIPIN-8 for disease models
In addition to the previously reported B-cell lymphoma and dermatitis pathologies, we will extensively examine the pathophysiological effects of HOIPIN-8. We will investigate the metabolism or physical properties of HOIPIN-8 in animals to determine the optimal method of administration, and study with disease models involving the protein aggregates (proteinopathy). Through these analyses, we will acquire the basic information for drug discovery targeting the M1 chain.
Publications
- *Iwasaki N, Terawaki S, Shimizu K, Oikawa D, Sakamoto H, Sunami K,Tokunaga F.
Th2 cell-derived histamine is involved in nasal Th2 infiltration in mice.
Inflamm Res. 70, 539-541 (2021)
PMID: 33811487 - Kuriyama Y, *Shimizu A, Kanai S, Oikawa D, Motegi SI, Tokunaga F, Ishikawa O.
Coordination of retrotransposons and type I interferon with distinct interferon pathways in dermatomyositis, systemic lupus erythematosus and autoimmune blistering disease.
Sci Rep. 11, 23146 (2021)
PMID: 34848794 - Hoang DV, Thuy LTT, Hai H, Hieu VN, Kimura K, Oikawa D, Ikura Y, Dat NQ, Hoang TH, Sato-Matsubara M, Dong MP, Hanh NV, Uchida-Kobayashi S, Tokunaga F, Kubo S, Ohtani N, Yoshizato K, *Kawada N.
Cytoglobin attenuates pancreatic cancer growth via scavenging reactive oxygen species.
Oncogenesis. 11, 23 (2022)
PMID: 35504863 - Hieu VN, Thuy LTT, Hai H, Dat NQ, Hoang DV, Hanh NV, Phuong DM, Hoang TH, Sawai H, Shiro Y, Sato-Matsubara M, Oikawa D, Tokunaga F, Yoshizato K, *Kawada N.
Capacity of extracellular globins to reduce liver fibrosis via scavenging reactive oxygen species and promoting MMP-1 secretion.
Redox Biol. 52, 102286 (2022)
PMID: 35334247 - Hara Y, *Ando F, Oikawa D, Ichimura K, Yanagawa H, Sakamaki Y, Nanamatsu A, Fujiki T, Mori S, Suzuki S, Yui N, Mandai S, Susa K, Mori T, Sohara E, Rai T, Takahashi M, Sasaki S, Kagechika, H, Tokunaga F, Uchida S.
LRBA is essential for urinary concentration and body water homeostasis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 119, e2202125119 (2022)
PMID: 35862451 - Oikawa D Gi M, Kosako H, Shimizu K, Takahashi H, Shiota M, Hosomi S, Komakura K, Wanibuchi H, Tsuruta D, Sawasaki T, *Tokunaga F.
OTUD1 deubiquitinase regulates NF-kB- and KEAP1-mediated inflammatory responses and reactive oxygen species-associated cell death pathways.
Cell Death & Disease. 13, 694 (2022)
PMID: 35941131 - Zhang Q, Terawaki S, Oikawa D, Okina Y, Usuki Y, Ito H, *Tokunaga F.
Suppression of Linear Ubiquitination Ameliorates Cytoplasmic Aggregation of Truncated TDP-43.
Cells. 11, 2398 (2022)
PMID: 35954242 - *Nakazawa S, Mamiya R, Kawabata-Iwakawa R, Oikawa D, Kaira K, Tokunaga F, Nobusawa S, Sato Y, Sasaki A, Yajima T, Shirabe K.
Identification and molecular analysis of HOIP Q622H germline polymorphism.
Oncol Lett. 24, 394 (2022)
PMID: 36276481 - *Yoshizato K, Taira T, Sato-Matsubara M, Sekiguchi S, Yabunaka Y, Kira Y, Ohashi T, Daikoku A, Ofusa K, Kadono C, Oikawa D, Matsubara T, Nakagama Y, Kido Y, Tokunaga F, Ikeda K, Kaneko A, Kawada N.
Cloaking the ACE2 receptor with salivary cationic proteins inhibits SARS-CoV-2 entry.
J Biochem. 172, 205-216 (2022)
PMID: 35792074 - Saito R, Tada Y, Oikawa D, Sato Y, Seto M, Satoh A, Kume K, Ueki N, Nakashima M, Hayashi S, Toyoshima Y, Tokunaga F, Kawakami H, *Kakita A.
Spinocerebellar ataxia type 17-digenic TBP/STUB1 disease: neuropathologic features of an autopsied patient.
Acta Neuropathol Commun. 10, 177 (2022)
PMID: 36476347
Former Publications
- Nakazawa S+, Oikawa D+, Ishii R+, Ayaki T, Takahashi H, Takeda H, Ishitani R, Kamei K, Izumi T, Kawakami H, Iwai K, Hatada I, Sawasaki T, *Ito H, *Nureki O, *Tokunaga F.
Linear ubiquitination is involved in the pathogenesis of optineurin-associated amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Nat. Commun. 7, 12547 (2016)
PMID: 27552911 - Oikawa D, Sato Y, Ohtake F, Komakura K, Hanada K, Sugawara K, Terawaki S, Mizukami Y, Phuong HT, Iio K, Obika S, Fukushi M, Irie T, Tsuruta D, Sakamoto S, Tanaka K, Saeki Y, Fukai S, *Tokunaga F.
Molecular bases for HOIPINs-mediated inhibition of LUBAC and innate immune responses.
Commun. Biol. 3, 163 (2020)
PMID: 32246052 - Oikawa D, Sato Y, Ito H, *Tokunaga F.
Linear ubiquitin code: Its writer, erasers, decoders, inhibitors, and implications in disorders.
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 3381 (2020)
PMID: 32403254 - Oikawa D, Hatanaka N, Suzuki T, *Tokunaga F.
Cellular and Mathematical Analyses of LUBAC Involvement in T Cell Receptor-mediated NF-kB Activation Pathway.
Front Immunol. 11, 601926 (2020)
PMID: 33329596 - Miyashita H+, Oikawa D+, Terawaki S, Kabata D, Shintani A, *Tokunaga F.
Crosstalk between NDP52 and LUBAC in innate immune responses, cell death, and xenophagy.
Front Immunol. 12, 635475 (2021)
PMID: 33815386