Yousuke Takaoka
Development of proteostasis modulators targeting the co-chaperon E3 ligase STUB1
 |
Susumu Goyama, MD, PhDDivision of Molecular Oncology, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences,The University of Tokyo |
|---|
Research summary
Proteostasis, the process by which cells control the abundance and folding of the proteome, is maintained by proteolytic systems. Dysregulation of proteostasis is a main feature of age-related diseases. STUB1 is a unique E3 ubiquitin ligase containing three tetratricopeptide repeats (TPR domains) at its N-terminal and a U-box domain at its C-terminal. The TPR domain mediates the interaction with cytoplasmic chaperones, such as HSP70 and HSP90, while the U-box domain interacts with E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes. Through the action of both domains, STUB1 has a pivotal role to maintain protein homeostasis by controlling chaperone levels and functions. However, the biological roles of the STUB1-HSP complexes are not fully understood. Furthermore, no clinically proven drugs that modulate STUB1-HSP interactions have been developed.
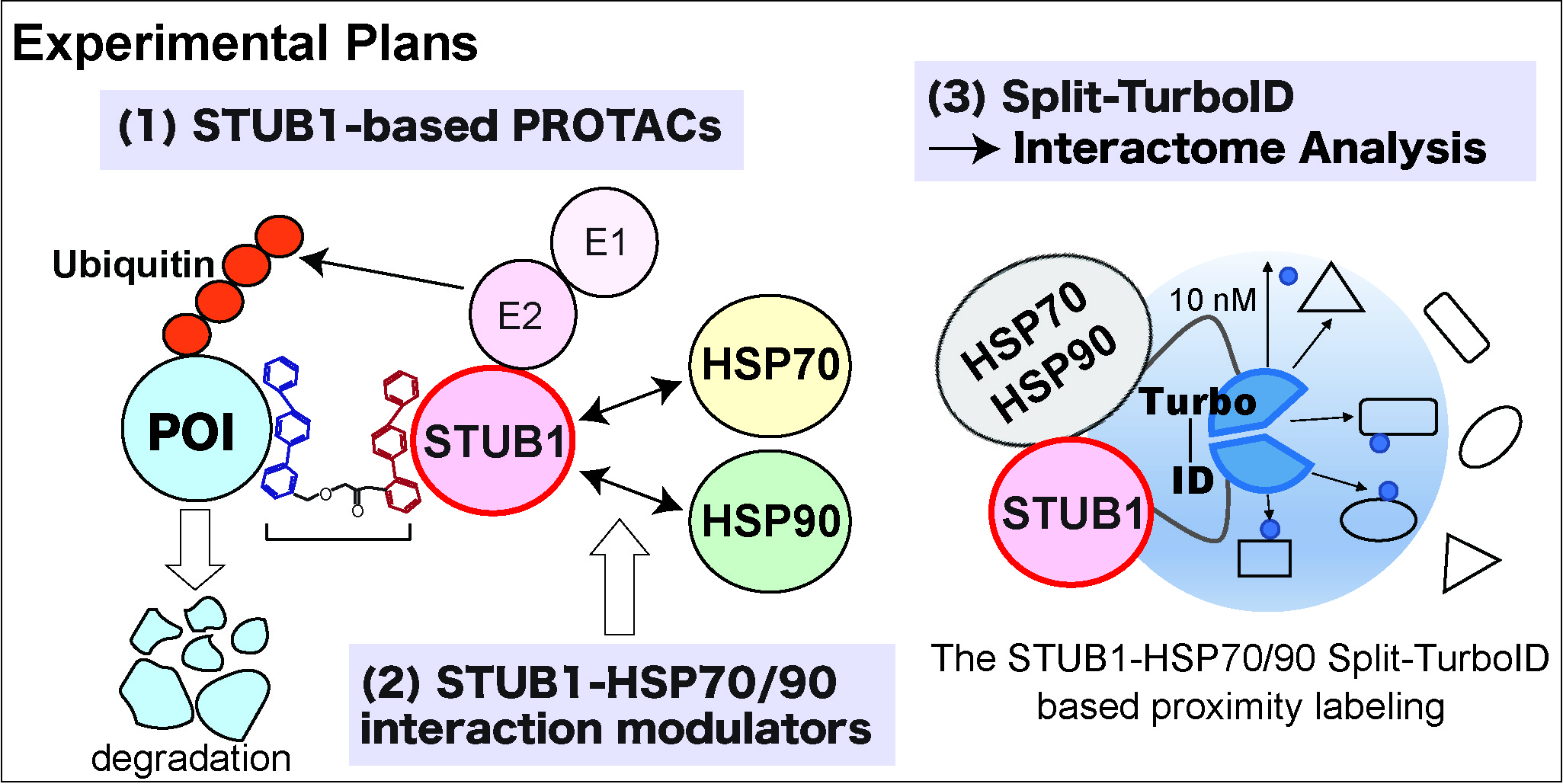
We previously showed that STUB1 promotes ubiquitination and degradation of the hematopoietic transcription factor RUNX1. Since then, we have been developing STUB1-targeting drugs and have identified 124 compounds that directly bind to STUB1 at the TPR domain. In this study, we aim to develop STUB1-based PROteolysis TArgeting Chimeras (PROTACs) that induce degradation of target proteins. Given that STUB1 plays a crucial role in protein quality control, the STUB1-based PROTACs could be superior to the currently available other PROTACs. We will also identify compounds that modulate interactions between STUB1 and the heat shock proteins using the wheat cell free alphascreen assay and the cell-based assays. Such compounds will be useful to modulate STUB1 functions in cells. Finally, we will investigate interactomes of STUB1/HSP70 and STUB1/HSP90 complexes using the cutting-edge Split-TurboID approach. Such information will tell us distinct roles of these complexes in the regulation of protein homeostasis. Together, we will develop novel drugs to regulate proteostasis through modulation of functions of the chaperone‐dependent E3 ubiquitin ligase STUB1.
Publications
- Yamamoto K, Goyama S, Asada S, Fujino T, Yonezawa T, Sato N, Takeda R, Tsuchiya A, Fukuyama T, Tanaka Y, Yokoyama A, Toya H, Kon A, Nannya Y, Onoguchi-Mizutani R, Nakagawa S, Hirose T, Ogawa S, Akimitsu N, *Kitamura T.
A histone modifier ASXL1 interacts with NONO and is involved in paraspeckle formation in hematopoietic cells.
Cell Rep. 36, 109576 (2021)
PMID: 34433054
Former Publications
- Goyama S, Yamamoto G, Shimabe M, Sato T, Ichikawa M, Ogawa S, Chiba S, *Kurokawa M.
Evi-1 is a critical regulator for hematopoietic stem cells and transformed leukemic cells.
Cell Stem Cell 3, 207-220 (2008)
PMID: 18682242 - Goyama S, Schibler J, Cunningham L, Zhang Y, Rao Y, Nishimoto N, Nakagawa M, Olsson A, Wunderlich M, Link KA, Mizukawa B, Grimes HL, Kurokawa M, Liu PP, Huang G, *Mulloy JC.
Transcription factor RUNX1 promotes survival of acute myeloid leukemia cells.
J. Clin. Investig. 123, 3876-88 (2013)
PMID: 23979164 - Goyama S, Wunderlich M, *Mulloy JC.
Xenograft models for normal and malignant stem cells.
Blood 125, 2630-2640 (2015)
PMID: 25762176 - Yonezawa T, Takahashi H, Shikata S, Liu X, Tamura M, Asada S, Fukushima T, Fukuyama T, Tanaka Y, Sawasaki T, Kitamura T, *Goyama S.
The ubiquitin ligase STUB1 regulates stability and activity of RUNX1 and RUNX1-RUNX1T1.
J. Biol. Chem. 292,12528-12541 (2017)
PMID: 28536267 - Hayashi Y, *Goyama S, Liu X, Tamura M, Asada S, Tanaka Y, Fukuyama T, Wunderlich M, O’Brien E, Mizukawa B, Yamazaki S, Matsumoto A, Yamasaki S, Shibata T, Matsuda K, Sashida G, Takizawa H, *Kitamura T.
Antitumor immunity augments the therapeutic effects of p53 activation on acute myeloid leukemia.
Nat. Commun. 10, 4869 (2019)
PMID: 31653912