Research Group
TeamResearch Group
Research group A01: Elucidation of ubiquitin functions by chemo-technologies
Ubiquitin structural biology providing the molecular basis for chemo-technologies
Shuya Fukai, D.Sc.Biological Structural Chemistry Group, Department of Chemistry, Graduate School of Science, Kyoto University |
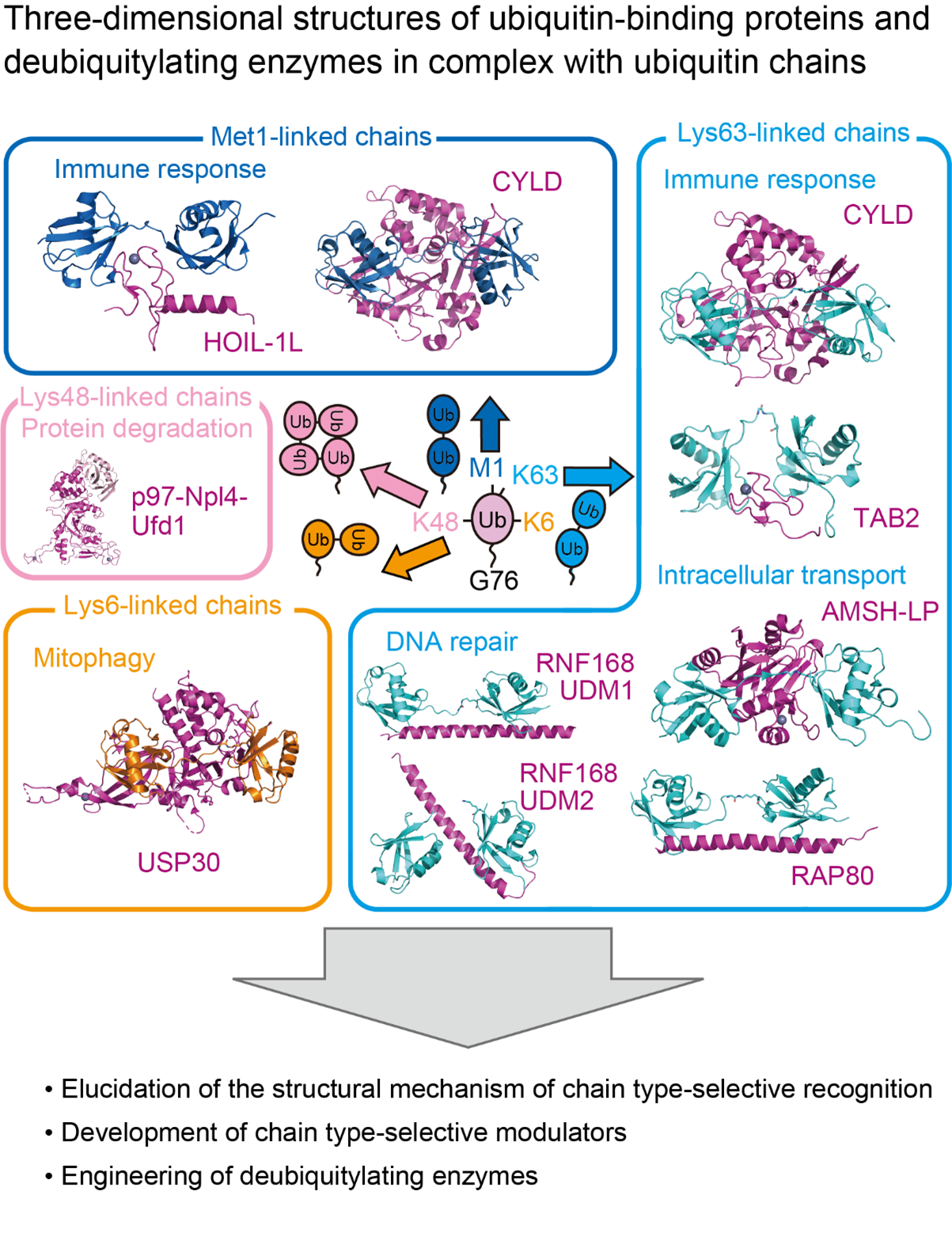
Ubiquitin modification plays essential roles not only in proteasomal degradation but also in other cellular functions such as inflammatory signaling and DNA damage response. In many cases, ubiquitin functions as a tandemly linked polymer termed “ubiquitin chain”, and varieties of the linkage type and other posttranslational modification (e.g., phosphorylation) combinatorially expand the functional information transmitted via the ubiquitin chain. In this research project, we determine three-dimensional structures of ubiquitin-binding domains (UBDs) and deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) in complex with ubiquitin chains to reveal novel mechanisms for ubiquitin chain recognition at atomic resolution. We also perform structural analyses of compounds that can regulate ubiquitin signaling to provide their mechanistic insights, which will aid further development of more efficient and/or functional compounds. Finally, we create molecular tools that are useful for ubiquitin research by modifying UBDs or DUBs.
1. Molecular basis provided from three-dimensional structure analysis
We determine ubiquitin chain-bound structures of UBDs or DUBs that recognize ubiquitin chains of specific linkage types, and structures of regulatory factors for ubiquitin signaling in action. Structural information will aid the development of compounds that can regulate ubiquitin signaling. Further structural analyses of such compounds in complex with their target proteins accelerate their improvement to achieve higher efficiency or multifunctionality.
2. Development of molecules that recognize specific chain types
We develop ubiquitin chain-binding molecules that can recognize a specific linkage type, based on the structural information of RAP80 tUIM or RNF168 UDM1/UDM2. These K63 chain-specific UBDs are composed of a single α-helix, whose mimics are likely to be stabilized by stapled peptide technique.
3. Engineering of DUBs
The Rpn11-Rpn8 DUB complex has an activity that can remove ubiquitin chains en bloc from polyubiquitinated polypeptides. We engineer this complex and create a molecular tool that can efficiently remove ubiquitin chains en bloc from various polyubiquitinated proteins.
Publications
- Okatsu K, Sato Y, Yamano K, Matsuda N, Negishi L, Takahashi A, Yamagata A, Goto-Ito S, Mishima M, Ito Y, Oka T, Tanaka K, *Fukai S.
Structural insights into ubiquitin phosphorylation by PINK1.
Sci. Rep. 8, 10382 (2018)
PMID: 29991771 - Takahashi TS, Sato Y, Yamagata A, Goto-Ito S, Saijo M, *Fukai S.
Structural basis of ubiquitin recognition by the winged-helix domain of Cockayne syndrome group B protein.
Nucleic Acids Res. 47, 3784-3794 (2019)
PMID: 30753618 - Sato Y, Tsuchiya H, Yamagata A, Okatsu K, Tanaka K, *Saeki Y, *Fukai S.
Structural insights into ubiquitin recognition and Ufd1 interaction of Npl4.
Nat. Commun. 10, 5708 (2019)
PMID: 31836717 - Yamanaka S, Sato Y, Oikawa D, Goto E, Fukai S, Tokunaga F, *Takahashi H, *Sawasaki T.
Subquinocin, a small molecule inhibitor of CYLD and USP-family deubiquitinating enzymes, promotes NF-κB signaling.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 524, 1-7 (2020)
PMID: 31898971 - Oikawa D, Sato Y, Ohtake F, Komakura K, Hanada K, Sugawara K, Terawaki S, Mizukami Y, Phuong HT, Iio K, Obika S, Fukushi M, Irie T, Tsuruta D, Sakamoto S, Tanaka K, Saeki Y, Fukai S, *Tokunaga F.
Molecular bases for HOIPINs-mediated inhibition of LUBAC and innate immune responses.
Commun. Biol. 3, 163 (2020)
PMID: 32246052 - *Takahashi H, Yamanaka S, Kuwada S, Higaki K, Kido K, Sato Y, Fukai S, Tokunaga F, *Sawasaki T.
A Human DUB Protein Array for Clarification of Linkage Specificity of Polyubiquitin Chain and Application to Evaluation of Its Inhibitors.
Biomedicines 8, 152 (2020)
PMID: 32512835 - Li Y, Okatsu K, Fukai S, *Sato Y.
Structural basis for specific recognition of K6-linked polyubiquitin chains by the TAB2 NZF domain.
Biophys J. 120, 3355-3362 (2021)
PMID: 34242591
Former Publications
- Sato Y, Yoshikawa A, Yamagata A, Mimura H, Yamashita M, Ookata K, Nureki O, Iwai K, Komada M, *Fukai S.
Structural basis for specific cleavage of Lys 63-linked polyubiquitin chains.
Nature 358-362 (2008)
PMID: 18758443 - Sato Y, Yoshikawa A, Mimura H, Yamashita M, Yamagata A, *Fukai S.
Structural basis for specific recognition of Lys 63-linked polyubiquitin chains by tandem UIMs of RAP80.
EMBO J. 28, 2461-2468 (2009)
PMID: 19536136 - Yoshikawa A, Sato Y, Yamashita M, Mimura H, Yamagata A, *Fukai S.
Crystal structure of the NEMO ubiquitin-binding domain in complex with Lys 63-linked di-ubiquitin.
FEBS Lett. 583, 3317-3322 (2009)
PMID: 19766637 - Sato Y, Yoshikawa A, Yamashita M, Yamagata A, *Fukai S.
Structural basis for specific recognition of Lys 63-linked polyubiquitin chains by NZF domains of TAB2 and TAB3.
EMBO J. 28, 3903-3909 (2009)
PMID: 19927120 - Sato Y, Fujita H, Yoshikawa A, Yamashita M, Yamagata A, Kaiser S E, *Iwai K, *Fukai S.
Specific recognition of linear ubiquitin chains by the Npl4 zinc finger (NZF) domain of the HOIL-1L subunit of the linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 20520-20525 (2011)
PMID: 22139374 - Sato Y, Yamagata A, Goto-Ito S, Kubota K, Miyamoto R, *Nakada S, *Fukai S.
Molecular basis of Lys-63-linked polyubiquitination inhibition by the interaction between human deubiquitinating enzyme OTUB1 and ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UBC13.
J. Biol. Chem. 287, 25860-25868 (2012)
PMID: 22679021 - Sato Y, Goto E, Shibata Y, Kubota Y, Yamagata A, Goto-Ito S, Kubota K, Inoue J, Takekawa M, Tokunaga F, *Fukai S.
Structures of CYLD USP with Met1- or Lys63-linked diubiquitin reveal mechanisms for dual specificity.
Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 22, 222-229 (2015)
PMID: 25686088 - Sato Y, Okatsu K, Saeki Y, Yamano K, Matsuda N, Kaiho A, Yamagata A, Goto-Ito S, Ishikawa M, Hashimoto Y, Tanaka K, *Fukai S.
Structural basis for specific cleavage of Lys6-linked polyubiquitin chains by USP30.
Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 24, 911-919 (2017)
PMID: 28945247 - Takahashi TS, Hirade Y, Toma A, Sato Y, Yamagata A, Goto-Ito S, Tomita A. *Nakada S, *Fukai S.
Structural insights into two distinct binding modules for Lys63-linked polyubiquitin chains in RNF168.
Nat. Commun. 9, 170 (2018)
PMID: 29330428