ユビキチンが形成するT細胞抑制性シグナルソームの分子イメージング解析

研究概要:
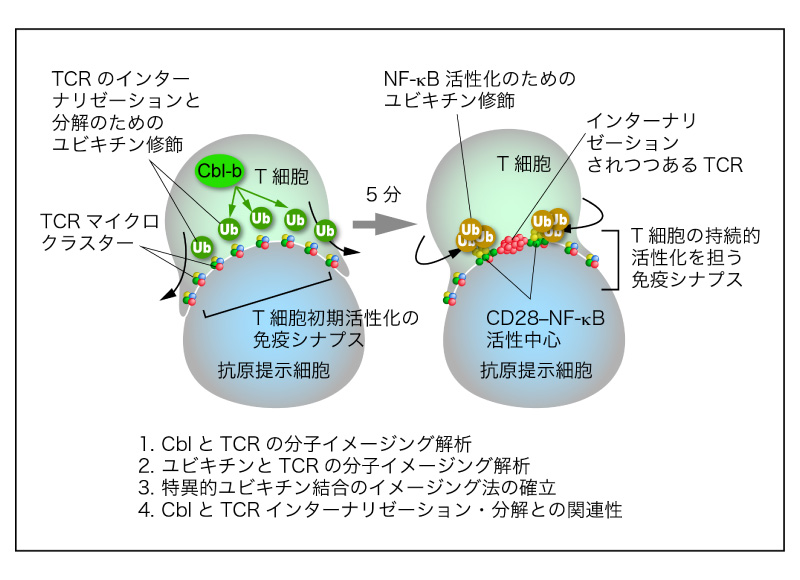
ユビキチン修飾は、蛋白分解・輸送、シグナル伝達などの翻訳後修飾系として、広く生命現象に関わっていますが、免疫担当細胞、特にT細胞においても、相反する二つの反応系、①T細胞受容体(TCR)のインターナリゼーションと分解によるTCRシグナルの終焉と、②NF-κB経路を介するT細胞活性化の持続、に重要です。我々はこれまで、T細胞が抗原提示細胞により活性される際、"TCRマイクロクラスター"と"CD28-NF-κB活性中心"という二つのシグナルソームが形成されること、また、負の副刺激受容体CTLA-4とPD-1も抑制性シグナルソームを形成し、相対する活性化クラスターを時空間的に制御することを見つけました。
本研究では、E3ユビキチンリガーゼCblファミリー分子とユビキチンの分子イメージング解析を行うことで、Cblのクラスター形成による新たなT細胞抑制メカニズムを解明しようと考えています。CblはT細胞のアナジーと深い関係にあるだけでなく、その変異が骨髄異形成症候群を誘導するなど、生理的な重要性も注目されており、自己免疫疾患のコントロールや癌治療へと繋がる分子基盤創出も視野に入れています。
関連する代表的な論文:
- 1. Hara, H., Yokosuka, T., Hirakawa, H., Ishihara, C., Yasukawa, S., Yamazaki, M., Koseki, H., Yoshida, H., and Saito, T. (2015) Clustering of CARMA1 through SH3-GUK domain interactions is required for its activation of NF-κB signalling. Nat. Commun. 6, 5555.
- 2. Kong, K.F., Fu, G., Zhang, Y., Casas, J., Yokosuka, T., Canonigo-Balancio, A.J., Becart, S., Kim, G., Yates, III J.R., Saito, T., Kronenberg, M., Gascoigne, N.R.J., and Altman, A. (2014) Protein kinase C-η controls CTLA-4-mediated regulatory T cell function. Nat. Immunol. 5, 465-472.
- 3. Liang, Y.†, Cucchetti, M.†, Roncagalli, R.†, Yokosuka, T.†, Malzac, A., Bertosio, E., Imbert, J., Nijman, I.J., Suchanek, M., Saito, T., Wülfing, C., Malissen, B., and Malissen, M. (†equally contributed authors) (2013) The lymphoid lineage-specific actin-uncapping protein Rltpr is essential for costimulation via CD28 and the development of regulatory T cells. Nat. Immunol. 14, 858-866.
- 4. Yokosuka, T.*, Takamatsu, M., Kobayashi-Imanishi, W., Hashimoto-Tane, A., Azuma, M., and Saito, T.* (*corresponding authors) (2012) Programmed cell death 1 forms negative costimulatory microclusters that directly inhibit T cell receptor signaling by recruiting phosphatase SHP2. J. Exp. Med. 209, 1201-1217.
- 5. Kong, K.F., Yokosuka, T., Canonigo-Balancio, A.J., Isakov, N., Saito, T., and Altman, A. (2011) A motif in the V3 domain of the kinase PKC-θ determines its localization in the immunological synapse and functions in T cells via association with CD28. Nat. Immunol. 12, 1105-1112.
- 6. Hashimoto-Tane, A., Yokosuka, T., Sakata-Sogawa, K., Sakuma, M., Ishihara, C., Tokunaga, M., and Saito, T. (2011) Dynein-driven transport of T cell receptor microclusters regulates immune synapse formation and T cell activation. Immunity 34, 919-931.
- 7. Yokosuka, T.*, Kobayashi, W., Takamatsu, M., Sakata-Sogawa, K., Zeng, H., Hashimoto-Tane, A., Yagita, H., Tokunaga, M., Saito, T. (*corresponding authors) (2010) Spatiotemporal basis of CTLA-4 costimulatory molecule-mediated negative regulation of T cell activation. Immunity 33, 326-339.
- 8. Yokosuka, T., Kobayashi, W., Sakata-Sogawa, K., Takamatsu, M., Hashimoto-Tane, A., Dustin, M.L., Tokunaga, M., and Saito, T. (2008) Spatiotemporal regulation of T cell costimulation by TCR-CD28 microclusters and protein kinase C theta translocation. Immunity 17, 589-601.
- 9. Varma, R., Campi, G., Yokosuka, T., Saito, T., and Dustin, M.L. (2006) T cell receptor-proximal signals are sustained in peripheral microclusters and terminated in the central supramolecular activation cluster. Immunity 25, 117-127.
- 10. Yokosuka, T., Sakata-Sogawa, K., Kobayashi, W., Hiroshima, M., Hashimoto-Tane, A., Tokunaga, M., Dustin, M.L., and Saito, T. (2005) Newly generated T cell receptor microclusters initiate and sustain T cell activation by recruitment of Zap70 and SLP-76. Nat. Immunol. 6, 1253-1262.