ユビキチン化を介した新たなリン酸化シグナル制御とストレス応答機構の解明

研究概要:
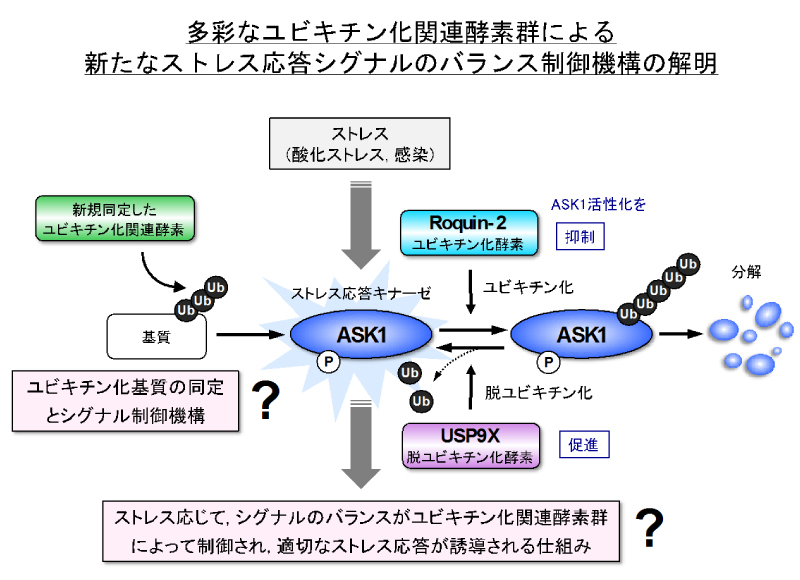
生命にとってストレスへの適応は不可欠であり、細胞はストレスの強さや種類に応じて、シグナルの強度やバランスを厳密に制御し、適切に応答する必要がありますが、その仕組みは良く分かっておりません。最近我々は、ストレス応答に関わるキナーゼの厳密な活性制御が、ユビキチン化関連酵素群によって行われること、特に免疫や酸化ストレス応答に重要なASK1キナーゼの活性化のバランスが、ユビキチン化酵素Roquin-2、脱ユビキチン化酵素USP9Xによって調節されることを明らかにしてきました。さらに、新たに同定した機能未知のユビキチン化酵素が、ASK1活性化に関わることを見出したことから、キナーゼに対して複数のユビキチン化関連酵素群が働き、異なる結合型のユビキチン化修飾などを介して、そのシグナルのバランス制御を行うことで、ストレスの強さや種類に応じた適切な応答が誘導される可能性があると考えられます。本研究では、新規同定したユビキチン化酵素の基質蛋白質の同定も含めてASK1活性調節機構を解明すると共に、それらユビキチン化関連酵素群による協調的なストレスシグナルのバランス制御を介して、適切なストレス応答が誘導される仕組みを分子レベルで明らかにし、ユビキチン化関連酵素を標的として、ストレス誘導性の細胞死や免疫応答の異常が原因となる免疫疾患や癌に対する新たな治療戦略開発に繋げたいと考えています。
関連する代表的な論文:
- Maruyama, T., Araki, T., Kawarazaki, Y., Naguro, I., Heynen, S., Aza-Blanc, P., Ronai, Z., Matsuzawa, A., and Ichijo, H. (2014) Roquin-2 promotes ubiquitin-mediated degradation of ASK1 to regulate stress responses. Sci. Signal. 7, ra8
- Mosallanejad, K., Sekine, Y., Ishikura-Kinoshita, S., Kumagai, K., Nagano, T., Matsuzawa, A., Takeda, K., Naguro, I., Ichijo, H. (2014) The DEAH-Box RNA helicase DHX15 activates NF-κB and MAPK signaling downstream of MAVS during antiviral responses. Sci. Signal. 7, ra40
- Naguro, I., Umeda, T., Kobayashi, Y., Maruyama, J., Hattori, K., Shimizu, Y., Kataoka, K., Kim-Mitsuyama, S., Uchida, S., Vandewalle, A., Noguchi, T., Nishitoh, H., Matsuzawa, A., Takeda, K., Ichijo, H. (2012) ASK3 responds to osmotic stress and regulates blood pressure by suppressing WNK1-SPAK/OSR1 signaling in the kidney. Nat. Commun. 3, 1285.
- *Tseng, P.H., *Matsuzawa, A., Zhang, W., Mino, T., Vignali, D.A., Karin, M. (2010) Different modes of ubiquitination of the adaptor TRAF3 selectively activate the expression of type I interferons and proinflammatory cytokines. Nat. Immunol. 11, 70-75.
- Maruyama, T., Kadowaki, H., Okamoto, N., Nagai, A., Naguro, I., Matsuzawa, A., Shibuya, H., Tanaka, K., Murata, S., Takeda, K., Nishitoh, H., and Ichijo, H. (2010) CHIP-dependent termination of MEKK2 regulates temporal ERK activation required for proper hyperosmotic response. EMBO J. 29, 2501-2514.
- Nagai, H., Noguchi, T., Homma, K., Katagiri, K., Takeda, K., Matsuzawa, A., and Ichijo, H. (2009) Ubiquitin-like sequence in ASK1 plays critical roles in the recognition and stabilization by USP9X and oxidative stress-induced cell death. Mol. Cell 36, 805-818.
- *Matsuzawa, A., *Tseng, P.H., Vallabhapurapu, S., Luo, J.L., Zhang, W., Wang, H., Vignali, D.A., Gallagher, E., and Karin, M. (2008) Essential cytoplasmic translocation of a cytokine receptor-assembled signaling complex. Science 321, 663-668.
- *Vallabhapurapu, S., *Matsuzawa, A., Zhang, W., Tseng, P.H., Keats, J.J., Wang, H., Vignali, D.A., Bergsagel, P.L., and Karin, M. (2008) Nonredundant and complementary functions of TRAF2 and TRAF3 in a ubiquitination cascade that activates NIK-dependent alternative NF-кB signaling. Nat. Immunol. 9, 1364-1370.
- Wang, H., Matsuzawa, A., Brown, S.A., Zhou, J., Guy, C.S., Tseng, P.H., Forbes, K., Nicholson, T.P., Sheppard, P.W., Häcker, H., Karin, M., and Vignali, D.A. (2008) Analysis of nondegradative protein ubiquitylation with a monoclonal antibody specific for lysine-63-linked polyubiquitin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 20197-20202.
- 10. *Matsuzawa, A., *Saegusa, K., Noguchi, T., Sadamitsu, C., Nishitoh, H., Nagai, S., Koyasu, S., Matsumoto, K., Takeda, K., and Ichijo, H. (2005) ROS-deepndent activation of TRAF6-ASK1-p38 pathway is selectively required for TLR4-mediated innate immunity. Nat. Immunol. 6, 587-592. * These authors contributed equally to this work.