RNF168によるK63結合型ポリユビキチン鎖特異的認識の構造的基盤

研究代表者:
佐藤 裕介
(東京大学・放射光連携研究機構・助教)
研究室HP:
http://www.iam.u-tokyo.ac.jp/srro/SRROLifeSciDivJp2/Top.html研究概要:
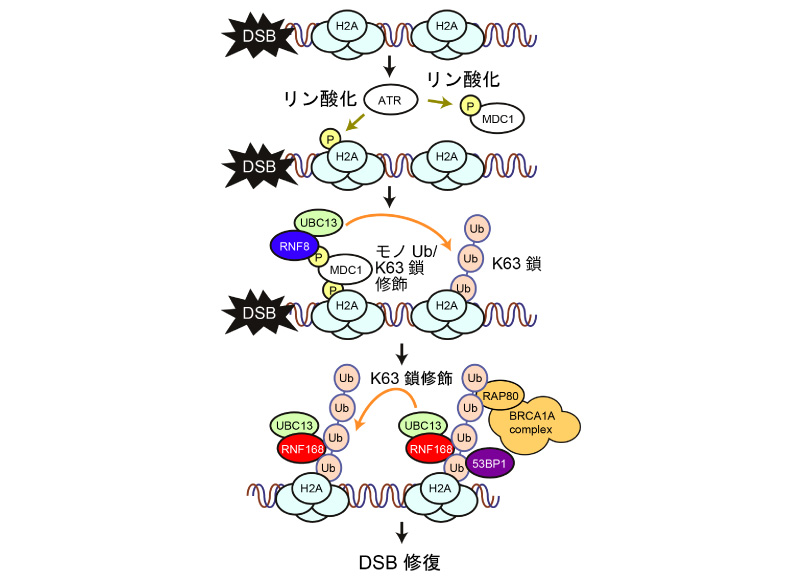
DNA二重鎖切断(DSB)はDNA両鎖の情報を同時に失う最も重篤なDNA損傷である。DSBの修復や細胞周期チェックポイントの制御は、E3ユビキチンリガーゼRNF8とRNF168によるクロマチンのUb化を介したシグナル伝達系が関わり、RNF168の変異は放射線感受性、免疫不全、異形症、学習障害などを特徴とするRIDDLE症候群の原因となる。
DSBが生じると、キナーゼATRによるリン酸化を引き金として、RNF8によってDSB近傍のヒストンH2AがK63Ub鎖修飾をうける。RNF168はUb結合領域を複数持ち、K63Ub鎖特異的に結合するため、Ub修飾をうけたクロマチンへと集積し、K63Ub鎖修飾を増幅する。K63結合型ポリUb鎖修飾はさらにRNF168をDSB近傍へと集積させる他、DSB修復に必要なRAP80-BRCA1A複合体や53BP1をDSB近傍に集積させる。
本研究ではRNF168とK63結合型Ub2量体の複合体の結晶構造解析を行う。さらに、変異体を用いた解離定数の測定、変異体の細胞内での局在の解析を行うことで、RNF168によるK63結合型Ub鎖の認識メカニズムとその意義を明らかにする。
関連する代表的な論文:
- Sato, Y., Goto, E., Shibata, Y., Kubota, Y., Yamagata, A., Goto-Ito, S, Kubota, K., Inoue, J., Takekawa, M., Tokunaga, F., and Fukai, S. (2015) Structures of CYLD USP with Met1- or Lys63-linked diubiquitin reveal mechanisms for dual specificity. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 22, 222-229.
- Toma, A., Takahashi, T.S., Sato, Y., Yamagata, A., Goto-Ito, S., Nakada, S., Fukuto, A., Horikoshi, Y., Tashiro, S., and Fukai, S. (2015) Structural basis for ubiquitin recognition by ubiquitin-binding zinc finger of FAAP20. PLoS One 10, e0120887.
- Sato, Y., Yamagata, A., Goto-Ito, S., Kubota, K., Miyamoto, R., Nakada, S., and Fukai, S. (2012) Molecular basis of Lys-63-linked polyubiquitination inhibition by the interaction between human deubiquitinating enzyme OTUB1 and ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UBC13. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 25860-25868.
- Sato, Y., Yamagata, A., Goto-Ito, S., Kubota, K., Miyamoto, R., Nakada, S., and Fukai, S. (2012) Molecular basis of Lys-63-linked polyubiquitination inhibition by the interaction between human deubiquitinating enzyme OTUB1 and ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UBC13. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 25860-25868.
- Sato, Y., Fujita, H., Yoshikawa, A., Yamashita, M., Yamagata, A., Kaiser, S.E., Iwai, K., and Fukai, S. (2011) Specific recognition of linear ubiquitin chains by the HOIL-1L NZF domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 20520-20525.
- Sato, Y., Yoshikawa, A., Yamashita, M., Yamagata, A., and Fukai, S. (2009) Structural basis for specific recognition of Lys 63-linked polyubiquitin chains by NZF domains of TAB2 and TAB3. EMBO J. 28, 3903-3909.
- Yoshikawa, A., Sato, Y., Yamashita, M., Mimura, H., Yamagata, A., and Fukai, S. (2009) Crystal structure of the NEMO ubiquitin-binding domain in complex with Lys 63-linked di-ubiquitin. FEBS Lett. 583, 3317-3322.
- Sato, Y., Yoshikawa, A., Mimura, H., Yamashita, M., Yamagata, A., and Fukai, S. (2009) Structural basis for specific recognition of Lys 63-linked polyubiquitin chains by tandem UIMs of RAP80. EMBO J. 28, 2641-2468.
- Sato, Y., Yoshikawa, A., Yamagata, A., Mimura, H., Yamashita, M., Ookata, K., Nureki, O., Iwai, K., Komada, M., and Fukai, S. (2008) Structural basis for specific cleavage of Lys 63-linked polyubiquitin chains. Nature 455, 358-362.